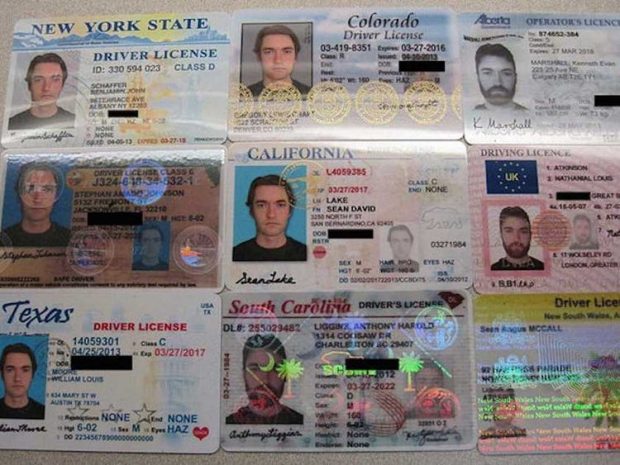
Fake ID sellers frequently advertise “Scannable” counterfeit IDs. As a result, it’s legitimate to wonder if an ID scanner will detect a fraudulent ID.
To answer this, you’ll need to know more about the technology behind various ID scanners, as well as the methods forgers can use to get around automated checks. The most common tests check an ID’s barcode or magnetic strip.

Barcodes Are for Data Collection
Most ID scanners read the information on the barcode or magnetic strip, and the data is checked to determine if it is returned in the correct format. Unfortunately, these characteristics are designed primarily to allow ID scanners to quickly extract information from an ID and are not intended to be strong security features.
With the needed technology and encoding methodologies available on the internet, fabricating barcodes and magnetic strips with correctly encoded identifying information is exceptionally straightforward. While cheap ID scanners may detect fake IDs, it’s rare for forgers to create IDs with incorrect barcodes or magnetic strips. Fake IDs offered on the most prominent internet marketplaces will all be authentic when scanned.
The majority of ID scanners in use today rely entirely on these checks, and the bulk of fake IDs in circulation pass these tests. To properly discover counterfeit IDs, you’ll need equipment that analyzes the ID’s face to spot minor flaws in the more advanced security mechanisms put into government-issued IDs.
An ID scanner can accurately identify fake IDs by comparing the pictures, typefaces, and spacing of scanned IDs to a real ID template using pixel-level analysis. It is something that just a few people are capable of. Pattern matching is the term for this sort of analysis.
How Do Fake ID Scanners Detect Fake IDs
When establishing official identification cards, issuers utilize sophisticated patterns and unique typefaces as crucial security measures to make them hard to copy correctly. To recreate the precise lines, distinctive fonts, micro text, and sophisticated graphics featured on an ID, illicit print companies need secure-held technology that isn’t generally available.
When these nuances are poorly imitated, the trained eye may immediately detect them. On the other hand, more complex fake IDs will often pass most human verifications. They can only be detected by examining the ID at such a granular level that only a few pixels typically reveal tell-tale signs of a fake.
Counterfeit identity papers are generating yearly rises in identity fraud losses among organizations worldwide, with access to these near-perfect fake IDs becoming more straightforward than ever on the dark web. Another layer of protection is holograms and fluorescent overlays, which allow ID scanners to perform a third test—the behavior of an ID’s reflective properties under various lighting situations.
Validating Holograms and Fluorescent Overlays
Holograms and fluorescent overlays are extra layers of security that may be evaluated by shining a white light on the ID or exposing it to UV light. Due to the ease with which these security measures may be validated using low-tech methods, the current counterfeiter will attempt to replicate them as precisely as possible. To fool these checks, forgers copy these security features or port over valid versions from actual IDs.
The quality of a counterfeit ID and the complexity of the ID scanner determine whether or not it will pass an ID scanner’s lighting test. More advanced fake IDs may duplicate holograms and fluorescent overlays, so relying on these checks alone might give you a false sense of security.
It’s All in the Scanning Engine
If the scanning engine isn’t powerful enough, fake IDs will pass all three checks. The scanning engine is the type of software that validates an ID by processing the data gathered by a scan.
A trustworthy scanning engine takes years to develop, is regularly updated, and employs millions of scans to create algorithms that successfully detect fraudulent ID. False positives are inevitable without a competent scanning engine, and subsequent versions of fake IDs will pass these tests.
You’ll need the necessary components to capture fake IDs using an ID scanner. To verify correctness, reliable tests look at the tiniest features on an ID. Pattern matching and a powerful scanning engine are the most critical components for confirming IDs.
Many firms’ ID scanners are simple to operate and need little to no training. Many consumers like the convenience, but much more so, they love not having to worry about their safety when they go out.
This is good news for patrons who previously felt uneasy about stepping out. True, ID scanners are expensive to install, but company owners that see them as an opportunity and an asset are better positioned to increase sales and reduce difficulties.
ID scanners have transformed the way bars, and nightclubs in the United States operate. Patron IDs are swiftly inspected and accepted, resulting in organized and fast-moving entrance lineups. The scanning systems flag fake IDs and those who shouldn’t be allowed in, and clients are less likely to conduct crimes as a result.
Even scanners with the correct hardware combination frequently fail to maintain their libraries up to date, resulting in difficulties such as reliability, false positives, and unreadable IDs. Will a counterfeit ID scan if all of the above factors are taken into account? Unfortunately, the answer is yes for most ID scanners.
Read More: